MATLAB
MATLAB[1] is installed on Picotte. To use:[2]
module load matlab
(or the appropriate version string).
Installed versions are: R20201a, R2020b, R2022b
Official Documentation♯
- Official documentation is online
Installed Toolboxes♯
To see the installed toolboxes, use the "ver" command within Matlab.
The Drexel Matlab license includes 33 toolboxes.[3]
Parallel Computing Toolbox♯
Picotte♯
t.b.a.
Proteus♯
To use the Parallel Computing Toolbox, you need to use the "matlab"
Parallel Environment. Detailed instructions are available in
$MATLABROOT/toolbox/distcomp/examples/integration/sge
Parallel jobs should use the "matlab" parallel environment. See below.
Using the Parallel Computing Toolbox consumes a license ("distrib_computing_toolbox"). See below.
MATLAB PATH and startup.m♯
By default, MATLAB includes ~/Documents/MATLAB in its search PATH. Any
startup commands may be placed in a file called startup.m in that
directory, i.e. ~/Documents/MATLAB/startup.m.
Interactive GUI Sessions♯
For both these cases, you must have the X11 software installed on your PC before you start.
Picotte♯
See: Running GUI Applications on Compute Nodes
GPU/CUDA Usage♯
The GPU Nodes on Picotte run CUDA 11.0.
For more information, see:
- MATLAB Official Documentation - GPU Computing
- Loren on the Art of Matlab Blog - Using GPUs in Matlab
GPU Example♯
Mathworks has an example of usage of GPUs (CUDA), and possible pitfalls: https://www.mathworks.com/help/parallel-computing/examples/illustrating-three-approaches-to-gpu-computing-the-mandelbrot-set.html
The example computes and displays a Mandelbrot set in three ways:
- using CPU only
- using the GPU in a naive manner
- using the GPU via a CUDA kernel (the proper way to use a GPU)
In order, here are the results of the three different methods of computing the Mandelbrot set:
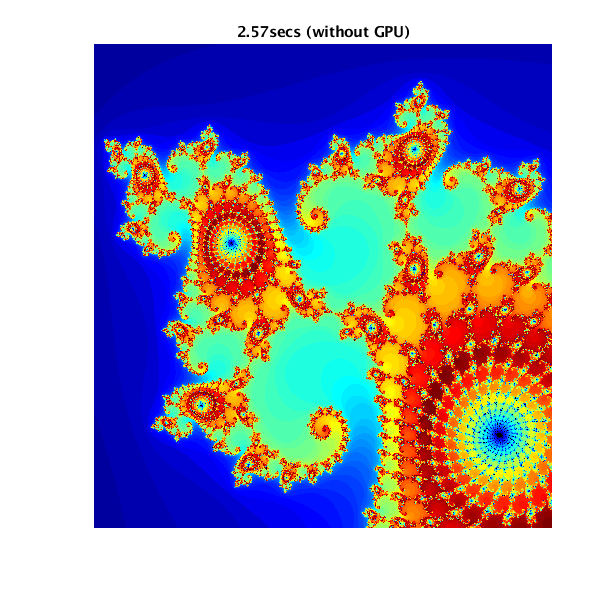
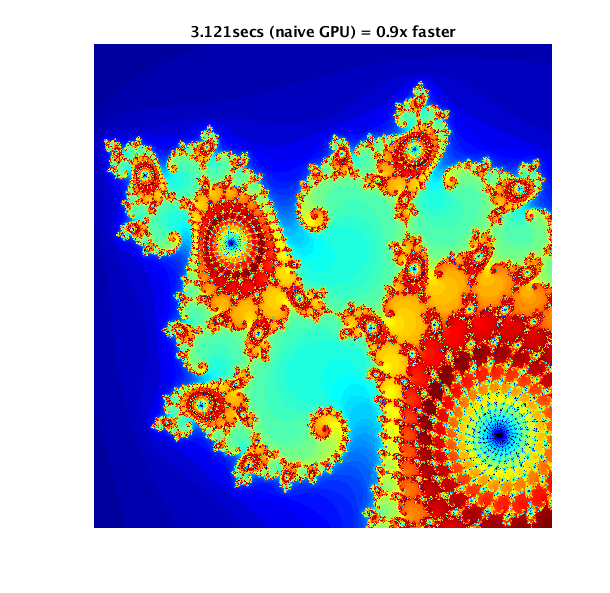
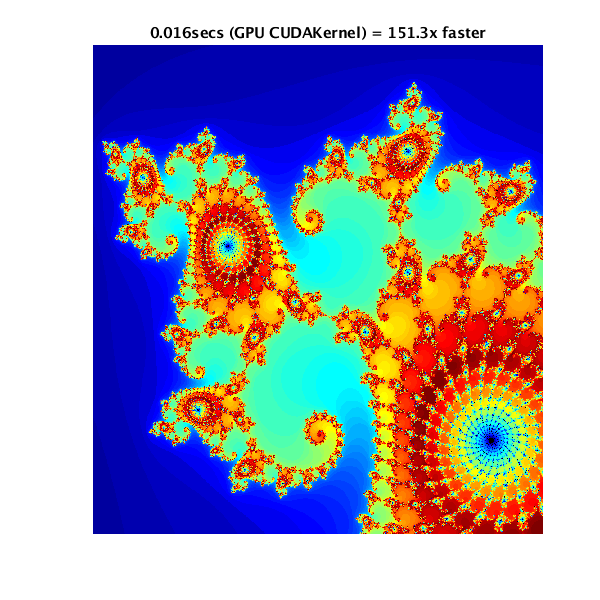
Job Scripts♯
Picotte Example♯
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --account=myrsrchPrj
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#SBATCH --ntasks=1
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=16
#SBATCH --mem=128G
#SBATCH --time=1:00:00
module load matlab
# Your Matlab program is a file named myprog.m
matlab -nodisplay -nodesktop -nosplash -noFigureWindows -r myprog
### Equivalently
#matlab -nodisplay -nodesktop -nosplash -noFigureWindows < myprog.m
### Number of Computation Threads - "Serial" Jobs
Matlab does not offer the user control over the number of threads of
computation. Some testing has shown that it will use all CPU cores up
**32**.
### Job Class
All Matlab jobs should not specify a PE request, and instead request the
"job class" (jc) named "matlab":
` #$ -jc matlab`
### Number of Slots
The number of slots can be read within Matlab by reading the environment
variable NSLOTS:
` n_slots = str2num(getenv("NSLOTS"))`
This may be used for setting `parpool` size. See [Parallel Execution](/MATLAB#Parallel_Execution) below.
### Reducing Memory Requirements
You may reduce memory requirements by not loading the Java Virtual
Machine[4] This may also speed up the startup process.
### Speeding Up Startup
MATLAB will run very slow if there are a lot of files (~10^5) in the
same directory where the "matlab" command is given. If you have a lot of
similar jobs to run, create a separate directory for each input, and
make sure to run the "matlab" command from that directory. (Thanks to Y.
Lan for figuring this out.)
For example, say you have a directory
`/mnt/HA/groups/myresearchGrp/TonsOfData/` containing 1 million data
files to be processed. The obvious way of doing this, i.e. create a job
script and a Matlab script in that directory and do a qsub there, will
result in very slow running. You should create the job script and the
Matlab script elsewhere, in a directory not containing so many files,
and do the qsub there. Matlab can open files with a full path:
``` matlab
% open a file using a full (explicit) path
fileID = fopen('/mnt/HA/myresearchGrp/TonsOfData/file001.txt', 'r');
doMyAnalysis(fileID, par1, par2);
Checkpointing♯
To checkpoint a job is to save the job's state such that it can be
stopped and restarted at the checkpoint. This is especially important
for Monte Carlo computations which run a long time: there is a
possibility the compute node may crash, or fail in some other way. It is
also a way to fit into the 48-hour global wallclock (h_rt) limit.
Your Matlab script should write a file, probably separate from your normal job output, containing checkpoint data. Checkpoint data are all items required to re-start the computation from that point. This may include things like seed values.
Parallel Execution♯
Please refer to the official Matlab Documentation[5]
If you use
parpool, you
should set the pool size to be the number of slots requested:
% read NSLOTS from environment -- this environment variable is set by the job scheduler, Grid Engine
% see the article on Writing Job Scripts#Environment Variables
poolsize = str2num(getenv('NSLOTS'));
parpool(poolsize);
parfor♯
The use of parfor[6] on the Proteus cluster is tricky because it may
lead to "oversubscription", unless one is careful. Oversubscription is
when a computation (or set of computations, in this case) execute more
threads than there are physical CPU cores.
If you have independent computations which you want to run simultaneously, we suggest using an array job: see Writing Job Scripts
Matlab's parfor uses a "pool" of CPU cores. Without the Matlab Parallel Server product, only local pools can be created. Parfor distributes computation to the CPU cores defined in a pool. If you run a job array, i.e. multiple tasks sharing one job ID each task on its own node, each task would create its own local parpool on its node.[7]
To use parfor, job- or task-specific local storage directories need to be set up. Matlab parfor stores state data and intermediate results in a subdirectory of your home directory. If multiple jobs are run simultaneously, the multiple jobs' parfor calls may overwrite each other's state data.
To make job- and task-specific local storage directories, you will need
to set up the JobStorageLocation. We recommend also to read the job
environment for the number of slots (CPU cores) for setting the number
of pool workers, rather than hard coding a literal number in the Matlab
code.
Each job that runs on Proteus has a node-local directory created for it
by Grid Engine. This directory is named by the job ID, task ID if
appropriate, and the queue name. This directory is also given by the
environment variable TMP. See Writing Job Scripts
Here is brief example to set the JobStorageLocation for parfor, and also the number of pool workers:[8][9]
% create a local cluster object
pc = parcluster('local')
% explicitly set the cluster JobStorageLocation
pc.JobStorageLocation = getenv('TMP')
% start the pool
% the environment variable NSLOTS is exactly what is set in your PE request;
% e.g. "#$ -pe shm 12" means that NSLOTS = 12
poolobj = parpool(pc, str2num(getenv('NSLOTS')))
parfor i = 1:100
ones(10,10)
end
% once computation is done, delete the pool object
% optional as objects are deleted at end of program
delete(poolobj)
This should be done before any parfor calls are made, whether in code you have written or in libraries you are using. This should only be done once per program.
No changes need to be made to your job scripts or resource requests. The
TMP directory is automatically deleted by Grid Engine upon job end.
Details about how Matlab executes parallel jobs are documented in the online Matlab manual.[10]
Compiling with MEX♯
The default GCC 4.8.1 may not be compatible with the MATLAB version you select. See Matlab - Supported and Compatible Compilers for the latest release of Matlab
[juser@proteusi01 ~]$ module unload gcc
[juser@proteusi01 ~]$ gcc --version
gcc (GCC) 4.4.7 20120313 (Red Hat 4.4.7-16)
Copyright (C) 2010 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This is free software; see the source for copying conditions. There is NO
warranty; not even for MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
In the same directory containing the source .c file, do the following:
[juser@proteusi01 MTIMESX]$ module load matlab/R2015b
[juser@proteusi01 MTIMESX]$ mex CFLAGS="-std=c99 -fPIC -O3" -DDEFINEUNIX -largeArrayDims -lmwlapack -lmwblas mtimesx.c
This produces a file named mtimesx.mexa64. Then, move the file the
your default MATLAB directory:
[juser@proteusi01 MTIMESX]$ mkdir -p ~/Documents/MATLAB
[juser@proteusi01 MTIMESX]$ mv mtimesx.mexa64 ~/Documents/MATLAB
And test it:
[juser@proteusi01 ~]$ matlab -nodisplay -nodesktop -nosplash
< M A T L A B (R) >
Copyright 1984-2015 The MathWorks, Inc.
R2015b (8.6.0.267246) 64-bit (glnxa64)
August 20, 2015
To get started, type one of these: helpwin, helpdesk, or demo.
For product information, visit www.mathworks.com.
Academic License
>> a = rand(4096);
>> b = rand(4096);
>> tic, c2 = mtimesx(a, b, 'speedomp'); toc
Elapsed time is 3.034698 seconds.
This example uses the MTIMESX package.
GPU/CUDA Support♯
- With CUDA 9, R2018a or later can be used
See Also♯
- MathWorks MATLAB Central -- online community for MATLAB and SimuLink users
- Oxford University Advanced Research Computing: Running Matlab
- MathWorks Academic Resource Kit -- provides live support for installation and a user self-service resource kit for downloads, updates, and free tutorials. Or call IRT Desktop Support at 215.895.2020
References♯
[3] Drexel IRT - Matlab Toolbox Licensing
[4] MATLAB Documentation: Disabling Java VM on startup
[5] MATLAB Documentation: Specify Your Parallel Preferences
[6] MATLAB Documentation: Parallel for loops (parfor)
[7] MATLAB Documentation: parpool
[8] Univ. of Chicago Research Computing Center - MATLAB
[9] Stanford Univ. FarmShare wiki - Matlab-parallel
[10] Matlab Documentation: How Parallel Computing Products Run a Job