Code Profilling
gprof Quick Start♯
gprof is known as a compiler that helps you understand where your code spent its time and what functions is called during the running time. It also generates the report in the graph format using grof2dot, which shows you in detailed how many times each function is called. To use gprof, follow the steps below:
Compiling♯
Recompile your code using the -pg argument to the compiler’s command line or add -pg to the FLAGS in the Makefile. This helps produce an executable which has debugging, and profiling turned on. Example: add -pg to the Makefile to generate the executable NB.run:
CC=g++ -std=c++11 -pthread
OPT=-O0 -pg
Generate gmon.out♯
After recompiling, run your program and wait until complete to create a gmon.out file. This gmon.out contains
Run gprof♯
Run the gprof using the command like this: gprof program-name gmon.out > gprof.out gprof.out is the output that will be examined later, or you can name it using your program’s name.
Analyzing the output♯
Format the report of gprof to be a graph using gprof2dot[1]: gprof2dot -s gprof.out | dot -Tpng -o output.png The output is a graph looks like this:
and side the graph:
+------------------------------------+
| function name |
| total time % ( self time % ) |
| total calls |
+------------------------------------+
where:
- total time % is the percentage of the running time spent in this function and all its children;
- self time % is the percentage of the running time spent in this function alone;
- total calls is the total number of times this function was called (including recursive calls).
An edge represents the calls between two functions and has the following layout:
total time %
calls
parent --------------------> children
Where:
- total time % is the percentage of the running time transferred from the children to this parent (if available);
- calls is the number of calls the parent function called the children.
Valgrind - Memcheck♯
Valgrind[2] is a tool that helps to debug and profile your program to make it run faster and more concise and accurate. This article shows you how to use Memcheck to detect many memory-related errors that may occur while running your program. These errors are common in C and C++ which may cause your program to crash.
Prepare your program♯
Compile your code using the -g following by one of these options: -O0, -O1
Run program with Memcheck♯
Run your program using this format: Valgrind - -leak-check-=yes myprogram arg1 arg2 Now your program will run slower and use more memory than regular (up to 30times slower).
Output♯
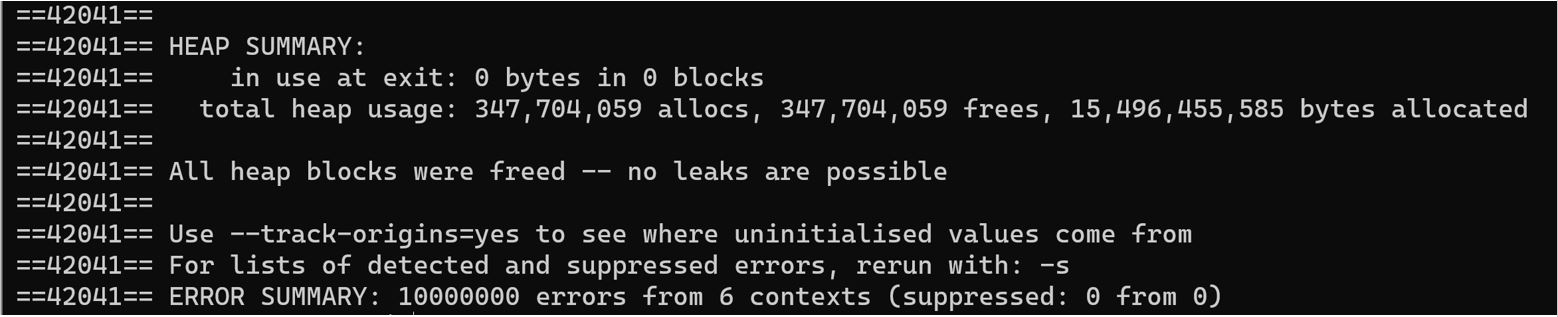
Common messages will have the format below:
Usually, the number 42041 is just the process id, so it is not important. These messages on the right side will contains a lot of important information, so read them carefully. Sometimes you will get a recommendation to rerun your program with different options to explore more about your program.
See also♯
References♯
[1] gprof2dot
[2] Valgrind